【Java】Java Web 之 Servlet
什么是 Servlet
Servlet 是 JavaEE 规范之一。规范就是接口
Servlet 就是 Java Web 三大组件之一
三大组件:
- Servlet 程序
- Fulter 过滤器
- Listener 监听器
Servlet 是运行在服务器上的一个 Java 小程序,可以接收客户端发送过来的请求,并且响应数据
第一个 Servlet 程序
1、因为 Servlet 是一个接口,所以首先需要编写一个类去实现 Servlet 接口
2、在类中实现 service 方法,处理请求并响应数据
3、到 web.xml 中配置 Servlet 程序的访问地址
新建一个类实现 Servlet 接口1
2
3
4
5
6public class HelloServlet implements Servlet {
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Hello Servlet");
}
}
在实现 Servlet 接口后,需要在 web.xml 中配置地址1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14<!-- servlet标签给Tomcat配置Servlet程序-->
<servlet>
<!--servlet -name标签Servlet程序起-一个别名(-般是类名) -->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!--servlet-class是Servlet程序的全类名-->
<servlet-class>com.haibara.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--servlet -mapping标签给servlet程序配置访问地址-->
<servlet-mapping>
<!--servlet-name标签的作用是告诉服务器,我当前配置的地址给哪个Servlet 程序使用-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!--urL-pattern标签配置访问地址-->
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
当项目运行起来时,在浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/servlet/hello 即可访问到 HelloServlet,在后台便会输出一句 “Hello Servlet”
URL 如何定位 Servlet 程序
以这个 URL 为例 http://localhost:8080/servlet/hello
- 通过 IP 定位服务器 ———————-> 通过 localhost 定位本机
- 通过端口定位软件 ———————-> 通过 8080 端口定位 Tomcat
- 定位工程路径 —————————-> 通过 /servlet 定位工程
- 定位资源 ———————————–> 通过 /hello 定位资源
- 通过 ServletName 定位类 ————->/hello 对应的是 HelloServlet 类
- 在 HelloServlet 中执行 service 方法
Servlet 生命周期
- 执行 Servlet 构造器方法
- 执行 init 初始化方法
- 执行 service 方法
- 执行 destroy 销毁方法
1 | public class HelloServlet implements Servlet { |
1 | 1、构造器方法 |
不难看出,首先是执行了 Servlet 的构造器方法,第二是执行 init 初始化方法,在此之后,访问 /hello 是执行了 service 方法,在创建好之后,多少次访问 hello 都无需在此调用构造器方法和初始化方法,都是调用的 service 方法,在关闭服务器时,会调用 destroy 方法进行销毁。
Servlet 的请求的分发处理
众所周知,请求分为通常有 GET/POST 两种形式(常用的),那么对于 GET 请求和 POST 请求后端需要进行区分,对不同的请求方式做不同的处理,那么 Servlet 如何实现的呢?
在 service 方法中,有一个 ServletRequest 类型的参数,可以通过它的子类去获取到请求的方式1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 通过ServletRequest的子类获取请求方式
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String method = request.getMethod();
if ("GET".equals(method)){
doGet();
}else if ("POST".equals(method)){
doPost();
}else {
System.out.println("反正不是GET请求和POST请求");
}
}
继承 HttpServlet 类实现 Servlet 程序
在实际应用中,只需要创建一个类并实现其中的 doGet 或 doPost 方法即可实现一个 Servlet 程序,可以在源码中看到,在 HttpServlet 类中的 service 方法已经做好了请求分发的工作。
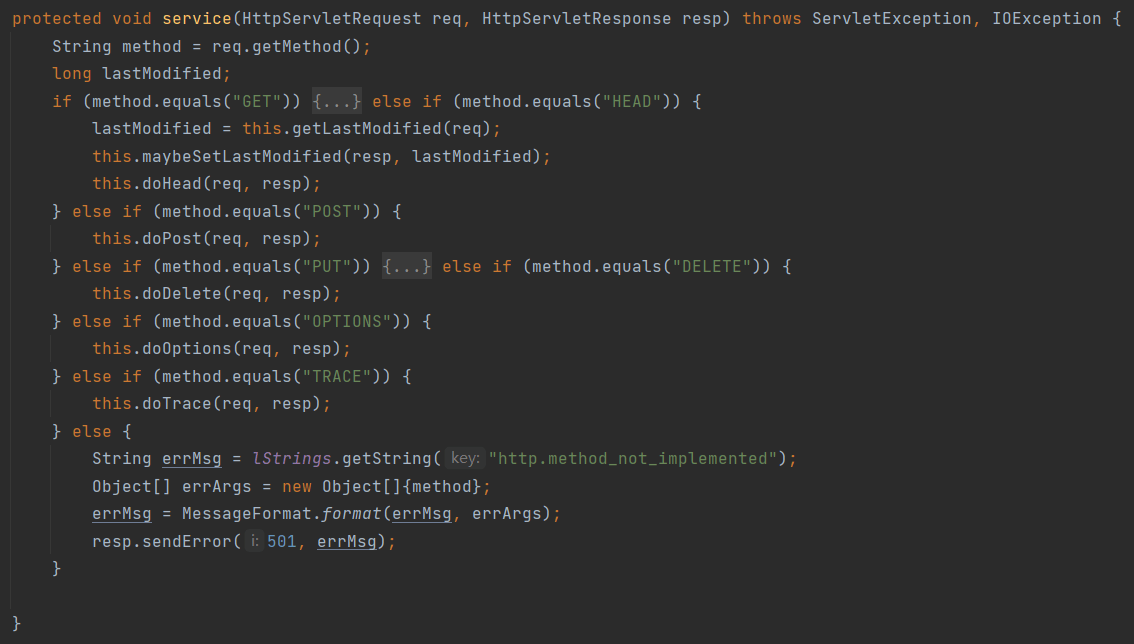
实现的过程分为三步:
1、继承 HttpServlet 类
2、重写 doGet/doPost 方法
3、在 web.xml 中配置 Servlet 程序访问地址1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class Servlet02 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doGet被调用");
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doPost被调用");
}
}
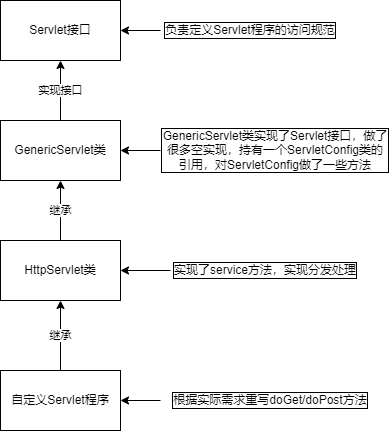
Servlet 整个类的继承体系
ServletConfig
ServletConfig 的三个主要作用
1、获取 Servlet 程序别名
2、获取初始化参数
3、获取 ServletContext 对象1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取Servlet程序别名
System.out.println(getServletConfig().getServletName());
// 获取初始化参数
System.out.println(getServletConfig().getInitParameter("username"));
// 获取ServletContext对象
System.out.println(getServletConfig().getServletContext());
}
ServletContext
什么是 ServletContext
1、ServletContext 是一 - 个接口, 它表示 Servlet 上下文对象
2、一个 web 工程,只有一个 ServletContext 对象实例。
3、ServletContext 对象是一个域对象。范围是整个工程
ServletContext 的作用
1、获取 web.xml 中配置的上下文参数上下文 - param
2、获取当前的工程路径,格式:/ 工程路径
3、获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径
4、像 Map- - 样存取数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1、获取web.xml中配置的上下文参数上下文-param
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String jdbc = servletContext.getInitParameter("jdbc");
System.out.println(jdbc);
// 2、获取当前的工程路径,格式:/工程路径
System.out.println(servletContext.getContextPath());
// 3、获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径
System.out.println(servletContext.getRealPath("/"));
}1
2
3jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/databases
/servlet
C:\AppHome\apache-tomcat-9.0.64\webapps\servlet\
操作域
1 | protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { |
1 | 操作context域之前null |
HttpServletRequest
HTTPServletRequest 的作用
Tomcat 在接收到 HTTP 请求后会将信息解析到 Request 对象中,并且传递到 service 方法中做分发处理,所以可以通过 HttpServletRequest 获取到请求的信息。
HTTPServletRequest 的常用方法
- getRequestURI () 获取请求的资源路径
- getRequestURL () 获取请求的统一资源定位符(绝对路径)
- getRemoteHost () 获取客户端的 ip 地址
- getHeader () 获取请求头
- getParameter () 获取请求的参数
- getParameterValues () 获取请求的参数(多个值的时候使用)
- getMethod () 获取请求的方式 GET 或 POST
- setAttribute (key, value); 设置域数据
- getAttribute (key); 获取域数据
- getRequestDispatcher () 获取请求转发对象
1 | protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { |
1 | /servlet/RequestTest |